The Muscular System.......BY Aveenash
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
OUR MUSCLES
- Enable us to move our body parts.
- Give us to our individual shape.
- Protect and keep in place our abdominal organs.
- Enable to us good posture.
- Help in our circulation of blood.
- Generate body heat when contract.
- .
TYPES OF MUSCLES
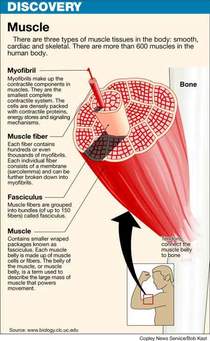
Skeletal muscles
Smooth Muscles
Cardiac Muscles
1: Skeletal or Voluntary Muscles:
- They are under our conscious control.
- Attached to skeleton by Tendons.
- Causes movement of bones at joints.
- they are fatigue.
- Perform every day action such as: walking, runing, jumping.
The major Skeletal Muscles:
- Deltoid, Biceps, Abdominals (4 muscles), Quadriceps (4 muscles), Pectorals, Latisimus dorsi, Trapizius, Triceps, Gluteals (3 muscles), Hamstrings (3 muscles), gastrocnemius.
2: Smooth or Involuntary Muscles:
- These Muscles work automatically- they are not our under consciuos control.
- Example: Muscles of Digestive System.
-
3: Cardiac Muscles:
- Cardiac muscles are special type of involuntary muscles.
- It is only foundst in Heart.
- It contracts regularly, continuosly and without tiring.
- It works automatically but is under constant Nervous and Chemical control.
- .
HOW DO OUR MUSCLES WORK?
- There are 3 main types of muscular contraction:
Isotonic and Concentric
Isotonic and Eccentric
Isometric
Isotonic and Concentric: Our muscles shorten as the contract.
- Example: The bicep during a pull-up.
- Most Sporting Movements are this type.
Isotonic and Eccentric: Our muscles lengthen as they contract under tension.
- Example: The bicep when we lower down from a pull-up.
Isometric: Our muscles stay the same length as they contract.
- There is no movement , so the ends of muscles stay the same distance apart.
- Example: Our Shoulder Muscles during a tug of war.
- .
MUSCLES CAN WORK AS:
- Flexors: Contracting to bend our joints.
- Extensors: Contracting to straighten joints
.
- Prime moovers (Agonists): Contracting to start a movement.
-
- Antagonists: Relaxing to allow movement to take place.
- Fixators: contracting to give the working muscles a firm base.
- Synergists: Stablising the area around the prime mover and fine tuning our movement.
MOVEMENT OF MUSCLES:
- Origin: The attachement of muscles to the bone that remains stationary.
-
- Insertion: The attachement of muscle to the bone that moves.
- Belly: The fleshy part of muscle between the tendons of origin and/ or insertion..
Muscles Disorders, Diseases and Injuries:
1: CRAMPS:
Involve sudden and violent muscles contractions. A person may experience painful cramps of certain skeletal muscles and smooth muscles.
2: MUSCLE SORENESS/Muscle strain:
Hard muscular may cause skeletal muscles become sore. In severe cases . the soreness may last up to four days. The muscle soreness may be due to the damage in muscle and connective tissue.
3: Muscle Diseases/Disorders:
a: Atrophy:
Diseases and damages the Brain or nerves that stimulate muscles.
b: Muscular dystrophy:
Is a serious disease that directly affects muscles. It weakness the skeletal muscles.
BY: Aveenash









No comments:
Post a Comment